|
| Architectural Layers | Defines for a organization |
| Business Architecture | Responsibilities : business process, organization, people |
| Data Architecture | Structures: logical and physical properties of data |
| Application Architecture | Defines: Applications functions, services, their interactions |
| Technology Architecture. | Provides: Hardware & software needed to develop, deliver, and integrate the services |
Service oriented architecture (SOA)
It is a style of software design uses communication protocols provide services to other components by application components in the network.
Application components -------------(Services)-------------> other components
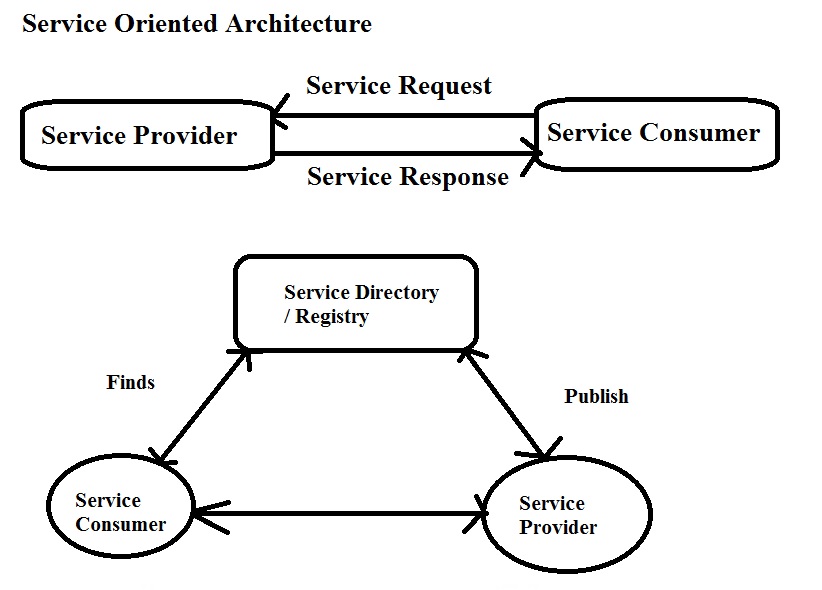
Roles within Service oriented Architecture
| Roles | Manages organization Services |
| Service provider | It provides details about Services (use, requirements, fees, what it Provides, Advertisement, registry published). |
| Service consumer | Service consumer is the user who locates services from service and use from the service provider. |
SOA Principles
| Principles | Details |
| Standardized service contract | Specified through 1 / more service description documents. |
| Loose coupling | Services dependencies on other services. |
| Abstraction | Hide implementation of logic. |
| Reusability | Reusing components, services reduces development time and costs. |
| Autonomy | Service consumer requires only the service to be used but not implementation. |
| Discoverability | It finds resources for utilization. |
| Composability | Business goals achieved by Creating services. |
SOA Advantages
| Advantage | Details |
| Reusability | Services reused by applications. |
| Easy maintenance | Services are independent, modified without affecting other services. |
| Platform independent | Services should run in any platform. |
| Availability | Request should be served |
| Reliability | SOA applications debugged easily. |
| Scalability | Services run on different servers within an environment. |
SOA Disadvantages
| Disadvantage | Details |
| Overhead | Services input parameters validation increases load, response time and decreases performance |
| Investment | SOA requires huge initial investment. |
| Service Management | Numbers of messages (millions) are exchanges between the services which is difficult to handle. |
Enterprise Software
Cloud ERP is Software as a Service that allows users to access Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software over the Internet.
| Software | Allows Users Access to Applications | Service Model | Use resources | Resources Maintained, Used, Cost | Cost |
| Cloud-Based Computing | Over Internet | Software As A Service | shared computing resources | remotely ,Leased, High | High |
| Cloud Erp | Over Internet | On Premises | Non sharable computing resources | Locally, on premises, Low | Low |
Benefits of Cloud ERP
| Benefit Name | Details |
| Pay Per Use Basis | Days / months / Years |
| Speed | Fast since no installation required (Hardware and software on servers or user devices). |
| Resources Adjustment | Dynamically |
| Backup And Recovery | Manual and Automatic |
| Attacks | Automatically avoid attack by Intruders |
| Remote Desktop | Facility available |
Home Back